ONLINE REVIEW VS.
CENTER EDITION VS.
BULLETIN BOARD KIT
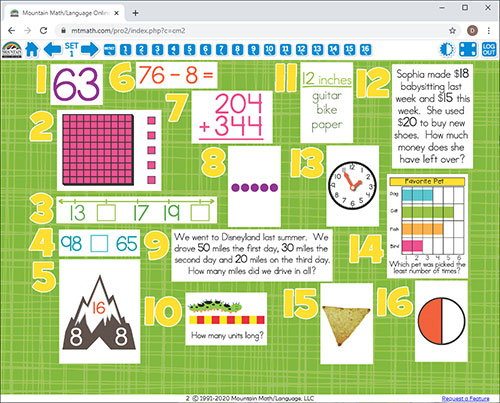
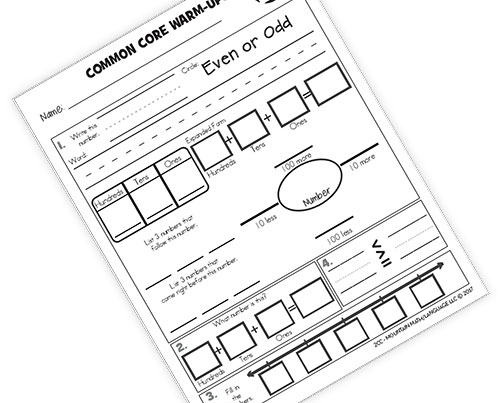
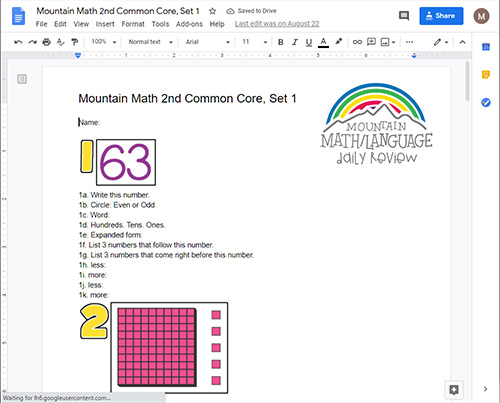
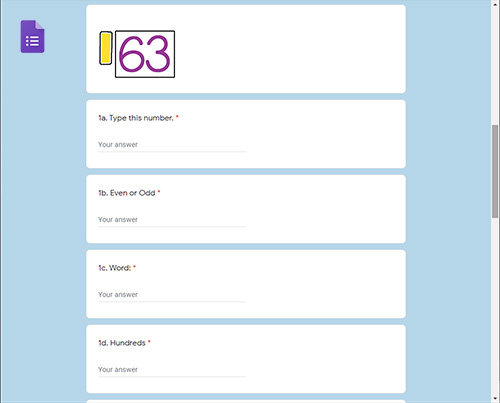
ONLINE REVIEW
Is projected onto an interactive white board, creating a virtual board. It can be viewed by the entire classroom.
Answers can be displayed onto the board at the click of a button. Up to seven questions can be isolated and magnified.
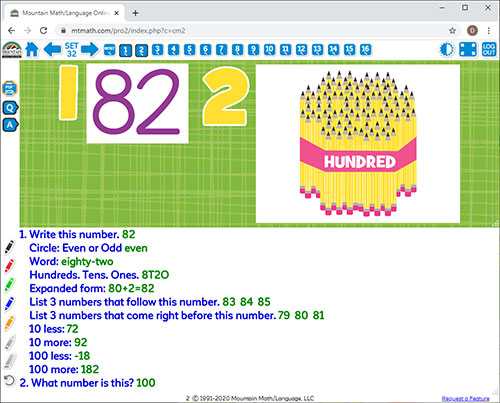
CENTER EDITION
Is organized on a 13"x19" flip chart. It can be viewed by 5-6 students at a time.
It was designed for small group review, such as rotations, scoots, centers, or math-around-the-classroom.
It has an answer key, heavy-duty stand, and high-gauged coil.
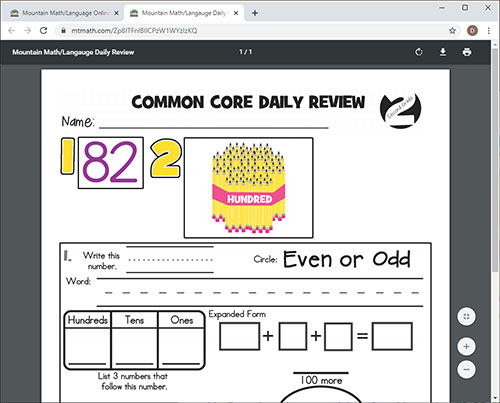
BULLETIN BOARD KIT
It is designed for total classroom view. It hangs on bulletin boards, walls, white boards, pocket charts,
and science display boards. Once hung, it can remain displayed for the entire year.
The cards can be interchanged, creating flexible and adjustable DAILY REVIEW.

 Online Review Sign In
Online Review Sign In